The Growing Impact of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain isn’t just some “occasional nuisance”—it’s a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide, from athletes to desk workers and everyone in between. Imagine the frustration of not being able to lift your child, play your favorite sport, or even just to sleep comfortably at night. For many, these are everyday realities, and the ripple effect on their quality of life is astronomical. Traditional treatments can help, but they often come with some limitations. Recovery can be slow, and sometimes, the pain lingers or returns.
But what if there was a way to tap into your body’s natural ability to heal? This is where stem cell therapy comes into the picture, offering an advantageous, non-invasive option for shoulder pain relief, including conditions like rotator cuff injury. In this article, we’re going to explore the incredible potential of stem cell therapy, how it works, and why it’s becoming a game-changer in treating shoulder pain.
We’re going to dive into the specifics; so, if shoulder pain has been holding you back, keep reading—you might just find the solution you’ve been searching for.
Statistics & Impact of Shoulder Pain and Injury

Shoulder pain is far more prevalent than many realize. In fact, it’s estimated that around 18-26% of adults will experience shoulder pain at some point in their lives, making it one of the most common musculoskeletal complaints. This issue doesn’t just affect athletes or those in physically demanding jobs—shoulder pain can strike anyone, from office workers to retirees, disrupting daily activities and overall quality of life.
One of the most concerning aspects of shoulder injuries is their tendency to linger. Studies show that up to 50% of people with shoulder pain may continue to experience symptoms after six months, and nearly 40% report ongoing discomfort even after a year. This residual pain often results in a cycle of rest, rehabilitation, and recurrence, where the injury never fully heals, leading to chronic pain and limited mobility.
Rotator cuff injuries are a major contributor to these statistics. They account for nearly 70% of all shoulder pain cases, with millions of people seeking medical attention for this type of injury every year. The impact is significant—not just in terms of physical discomfort, but also in the way it can affect mental health and daily life. Persistent shoulder pain can lead to sleep disturbances, decreased work productivity, and even depression or anxiety.
Understanding the Shoulder Joint
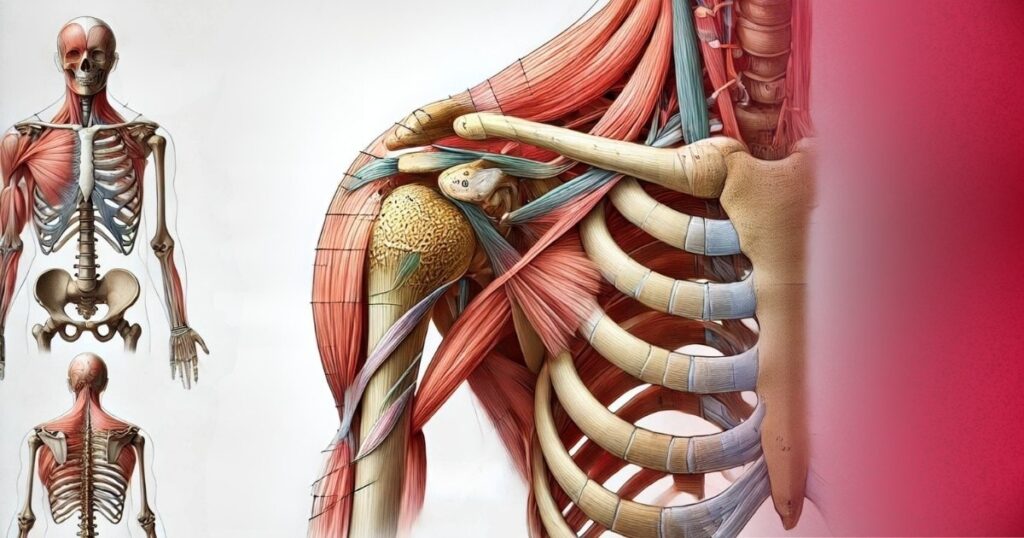
Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder joint is one of the most complex and mobile joints in the human body, allowing for a wide range of motion. It’s a ball-and-socket joint formed where the humerus (the upper arm bone) fits into the scapula (shoulder blade). The shoulder joint is stabilized by a group of muscles and tendons known as the rotator cuff, which helps keep the head of the humerus firmly within the shallow socket of the scapula. The rotator cuff tendon plays a crucial role in stabilizing the shoulder joint and is particularly susceptible to injuries. Additionally, the joint is supported by ligaments, the labrum (a cartilage ring that deepens the socket), and bursae (fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between tissues).
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain can be caused by various conditions, ranging from acute injuries to chronic degenerative processes. Some of the most common causes include:
Rotator Cuff Injuries: Tears or inflammation in the tendons of the rotator cuff are a leading cause of shoulder pain, especially in people who perform repetitive overhead activities.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: This occurs when the rotator cuff tendons are compressed during arm movements, leading to pain and inflammation.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can cause the breakdown of cartilage in the shoulder joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis): Frozen Shoulder is characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, often developing gradually and limiting the range of motion.
Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae can cause pain, especially with movement, due to increased friction within the joint.
Dislocations and Fractures: Traumatic injuries can result in the dislocation of the shoulder joint or fractures of the bones, leading to severe pain and instability.
3. Conventional Treatments for Shoulder Pain
Rest, Ice, and Physical Therapy
The first line of treatment for shoulder pain typically involves conservative measures like rest, ice, and physical therapy. Resting the shoulder allows the inflamed tissues to heal, while ice helps reduce swelling and pain. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in restoring mobility and strength to the shoulder, often involving exercises designed to improve range of motion and stabilize the joint. However, these treatments can be slow, and some patients may experience only partial relief or find that their symptoms return after activity is resumed.
Shoulder Surgery
When simple, conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, or in cases of severe injury, surgical intervention may be considered. Common shoulder surgeries include rotator cuff repair, shoulder arthroscopy to remove bone spurs or repair torn tissues, and shoulder replacement for cases of severe arthritis. While surgery can be effective, it is invasive, requires a lengthy recovery period, and carries the risk of complications such as infection, stiffness, and persistent pain. Some patients may also find that surgery does not completely resolve their symptoms, leading them to explore alternative treatment options.
Stem Cell Therapy
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are like the body’s versatile apprentices—ready to take on any job where they’re needed. Whether it’s repairing a torn muscle, forming new blood cells, or creating nerve pathways, these adaptable cells can transform into nearly any type of cell in the body. Their unique ability to step in and heal is what makes them so vital in cutting-edge medical treatments.
Types of Stem Cells Used
In the context of stem cell therapy for shoulder pain, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are the primary type used. Adult stem cells are typically harvested from the patient’s own body, either from bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue. Using autologous stem cells, which are harvested from the patient’s own body, minimizes risks such as immune rejection and infection. Bone marrow-derived MSCs are obtained through a minimally invasive procedure, usually from the pelvis.
Adipose-derived MSCs are collected via liposuction from areas such as the abdomen or thighs. Both types of MSCs are prized for their regenerative capabilities, as they can differentiate into various types of musculoskeletal tissues, including bone, cartilage, and tendon, making them ideal for repairing damaged shoulder tissues.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works
Stem cell therapy involves several key steps, starting with the extraction of stem cells from the patient’s own body. These cells are typically harvested from bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue through a minimally invasive procedure. Once collected, the stem cells are processed and concentrated in a laboratory to ensure they are in their most potent and effective form. During this processing, red blood cells and white blood cells are separated from the stem cells to ensure the most potent and effective form of treatment.
After preparation, the concentrated stem cells are then injected directly into the affected area of the body, such as a joint, muscle, or tendon, where tissue damage or degeneration has occurred.
Once the stem cells are delivered to the target area, through injection, they begin their work in promoting tissue regeneration. They can differentiate into the specific types of cells needed to repair the damaged tissue, such as cartilage, bone, or muscle cells. Additionally, stem cells release growth factors that reduce inflammation and stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, further aiding in tissue repair and recovery. Taking the approach of stem cell therapy not only helps alleviate pain but also addresses the underlying cause of the problem, offering a more lasting and effective solution compared to traditional treatments.
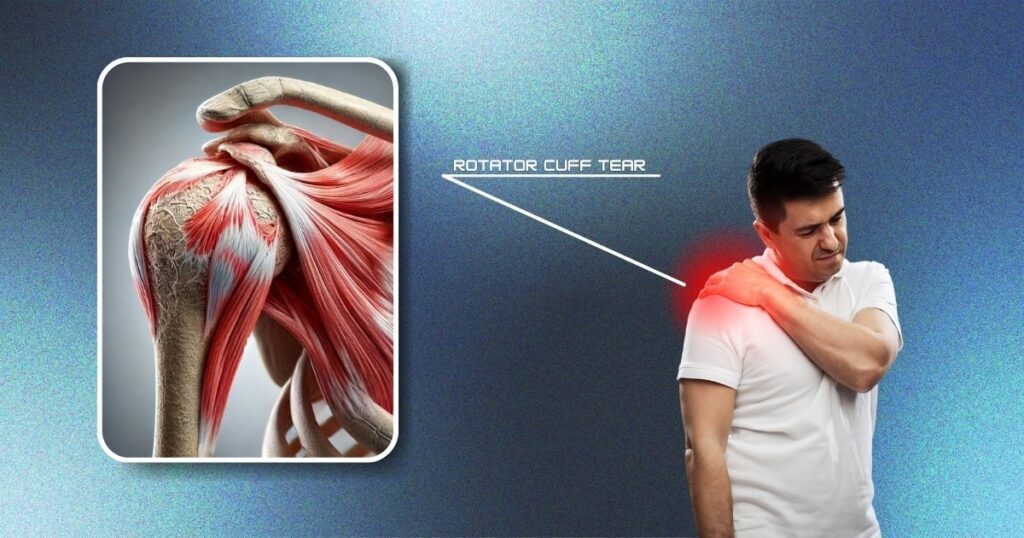
Stem Cell Therapy for Rotator Cuff Injuries
Understanding Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff injuries are a common source of shoulder pain, particularly among individuals who engage in repetitive overhead activities, such as athletes and manual laborers. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their associated tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and allow for a wide range of motion. Rotator cuff injuries can range from inflammation (tendinitis) and impingement to partial or complete tears of the tendons. These injuries can cause significant pain, weakness, and limited range of motion, severely impacting daily activities and quality of life. Over time, if left untreated, rotator cuff injuries can worsen, leading to chronic pain and further degeneration of the shoulder joint.
Treating rotator cuff injuries presents several challenges. While conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications can provide relief, they often fail to fully heal the damaged tendons, especially in cases of significant tears. Surgical intervention is an option, particularly for severe, torn rotator cuff injuries, but it is not without risks. Surgery requires a long recovery period, with some patients experiencing stiffness, limited mobility, or even re-injury after the procedure. Additionally, surgery may not completely restore the function of the shoulder, leaving patients with lingering pain or weakness. These limitations highlight the need for alternative treatments that can not only relieve pain but also promote true healing and restoration of the injured tissues.
Stem Cells in Accelerating Recovery
Stem cell therapy offers a promising alternative for accelerating the recovery of rotator cuff injuries. When injected into the damaged rotator cuff area, stem cells can help regenerate the torn tendons by differentiating into tendon-like cells and promoting the formation of new, healthy tissue. Stem cell shoulder injections are used to deliver stem cells directly to the damaged area, promoting tissue regeneration and healing. Additionally, stem cells release growth factors that reduce inflammation and enhance the body’s natural healing processes, potentially leading to faster and more complete recovery. Unlike traditional treatments, which primarily focus on managing symptoms, stem cell therapy targets the root cause of the injury, aiming to repair the damage and restore full function to the shoulder. This regenerative approach has the potential to reduce recovery times, minimize the need for invasive surgery, and provide longer-lasting relief.
Case Studies & Research
Research and clinical studies on stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries have shown promising results. Several studies have demonstrated that patients who received stem cell injections experienced significant improvements in pain, function, and tendon healing compared to those who underwent conventional treatments alone. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine found that patients treated with stem cell therapy following a rotator cuff tear surgery had a lower re-tear rate and better overall outcomes than those who received surgery alone. Other research has shown that stem cell therapy can enhance the healing process in partial rotator cuff tears, reducing the need for more invasive surgical procedures. While more research is needed to fully understand the long-term benefits, the current evidence suggests that stem cell therapy could be a game-changer in the treatment of rotator cuff injuries, offering patients a more effective and less invasive option for recovery.
The Procedure: What to Expect
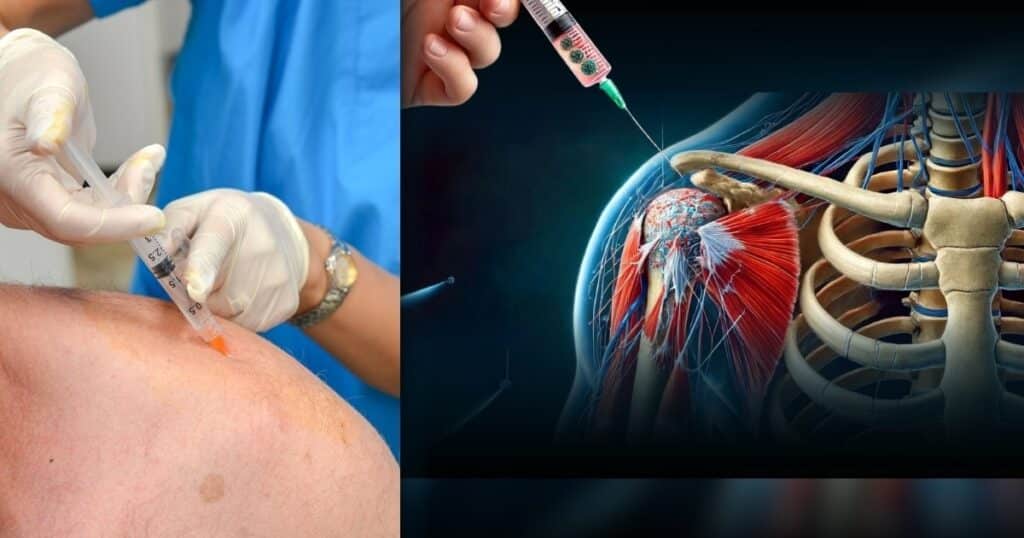
Initial Consultation and Evaluation
The first step is a one-on-one consultation with your doctor. This isn’t just a quick check-up; it’s a comprehensive discussion about your pain, your medical history, and how it’s affecting your life. Your doctor will carefully examine your shoulder, possibly using an MRI or ultrasound to get a detailed look at what’s going on inside. This isn’t just about finding the problem—it’s about understanding your unique situation and tailoring a treatment plan that’s right for you. By the end of this consultation, you’ll know whether stem cell therapy is a good fit for your needs.
Stem Cell Extraction and Preparation
Once you’ve decided to move forward, the next step is to harvest the stem cells that will help heal your shoulder. These cells are typically taken from your own body, which makes the process feel a bit more natural. Here’s how it works:
Bone Marrow Harvesting: If your stem cells are coming from bone marrow, your doctor will numb a small area near your pelvis. They’ll use a needle to withdraw the bone marrow, which only takes a few minutes. You might feel some pressure, but it’s generally quick and manageable.
Adipose Tissue Harvesting: If the cells are coming from fat tissue, it’s a similar story. After numbing the area—usually your abdomen or thighs—a small amount of fat is removed through a minor liposuction procedure. This is just as straightforward, and you’ll be up and about in no time.
The collected cells are then processed in a lab to concentrate them, making sure they’re as powerful and ready as possible for the task ahead. If the clinic decides to go with donor cells, you skip this step and go straight to the injection process.
Injection Process
Now comes the exciting part: delivering the stem cells to where they’re needed most. You’ll be back in the doctor’s office for this, where they’ll use advanced imaging technology to guide the injection precisely into the damaged area of your shoulder. The process is quick—usually less than an hour—and while you might feel a bit of discomfort, it’s often described as no worse than getting a flu shot. Many patients are surprised at how easy this part is, and you can head home shortly afterward.
Post-Procedure Care
After the injection, you’ll need to take it easy for a bit—think of it as giving your shoulder a chance to start healing. You might feel some soreness for a few days, similar to the feeling after a good workout, but this is a sign that your body is starting to respond. Your doctor will give you detailed instructions, which might include gentle exercises to keep your shoulder moving without overdoing it. Regular check-ins with your doctor will help track your progress and ensure everything is on the right track. Most people find that they can gradually return to their normal activities, feeling better as the weeks go by.
Benefits and Potential Risks of Stem Cell Therapy.
Advantages Over Conventional Treatments
Stem cell therapy isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a real, science-backed option that’s changing how we think about healing. But like any medical treatment, it’s important to understand both the upside and the potential downsides
There’s a lot to love about stem cell therapy, especially when compared to traditional treatments:
Less Invasive: No one likes the idea of surgery, with its long recovery times and the potential for complications. Stem cell therapy offers a non-surgical option that’s much easier on your body.
Natural Healing: Because the stem cells come from your own body, they work with your natural healing processes, promoting real, lasting repair rather than just masking symptoms.
Quicker Recovery: Many patients find they’re back to their usual activities much faster than they would be after surgery. This means less time off work or away from the things you love.
Reduced Dependency on Meds: Chronic pain often leads to long-term use of painkillers, which come with their own risks. Stem cell therapy targets the root of the problem, potentially reducing or even eliminating the need for ongoing medication.
Research supports these benefits. Studies have shown that stem cell therapy can significantly improve shoulder function and reduce pain, particularly for conditions like rotator cuff injuries. For instance, one study in the American Journal of Sports Medicine found that patients who had stem cell therapy after rotator cuff surgery experienced better healing and fewer re-tears than those who didn’t.
Risks and Considerations
No treatment is without risks, and it’s important to go in with your eyes open:
Infection: Anytime you have an injection, there’s a small risk of infection. However, this is rare and can usually be managed with antibiotics if it does occur.
Temporary Discomfort: Some patients report feeling soreness or swelling at the injection site. This is usually short-lived and can be managed with simple pain relievers.
Varied Results: Not everyone responds to stem cell therapy in the same way. Factors like the severity of your injury, your overall health, and how your body responds to the treatment all play a role in how well it works.
Cost: Stem cell therapy can be expensive, and not all insurance plans cover it. This is something you’ll want to discuss with your doctor and your insurance provider before moving forward.
Ethical Considerations: Our therapy uses autologous adult stem cells, avoiding the ethical concerns associated with fetal stem cells.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Stem Cell Therapy?
Ideal Candidates For Shoulder SCT
Deciding whether stem cell therapy is the right option for you involves more than just a desire to try something new. It’s about understanding who can truly benefit from this innovative treatment and knowing when it might not be the best choice.
Stem cell therapy is particularly promising for individuals who have shoulder pain due to specific types of injuries or conditions. If you’ve been struggling with issues like:
Rotator Cuff Tears: Whether it’s a partial tear or something more severe, stem cell therapy can help accelerate healing by promoting tissue regeneration.
Arthritis: If you’re dealing with osteoarthritis in your shoulder, where the cartilage is wearing down, stem cells might help by regenerating cartilage and reducing inflammation.
Tendonitis or Bursitis: Chronic inflammation in the tendons or bursae that hasn’t responded well to physical therapy or medication can often benefit from stem cell therapy’s regenerative effects.
In general, if you’ve tried conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, or medications and still haven’t found relief, you might be a good candidate for stem cell therapy. It’s also a strong option if you’re hoping to avoid or delay surgery, especially if your shoulder pain is significantly impacting your daily life.
However, being an ideal candidate isn’t just about your physical condition. It’s also about your mindset. Patients who are open to following post-procedure care instructions and are committed to a gradual recovery process tend to see the best results.
Contraindications What Can Prevent You From Being A Candidate
While stem cell therapy is safe for many people, it’s not for everyone. There are certain conditions and situations where this treatment might not be appropriate:
Severe or Advanced Conditions: If your shoulder joint is severely damaged, with extensive cartilage loss or very large rotator cuff tears, stem cell therapy might not be enough on its own. Surgery could be necessary in these cases.
Infections or Cancer: Specific active infections and certain types of cancer can make stem cell therapy unsafe. Your doctor will evaluate these risks carefully.
Blood Disorders: If you have a blood clotting disorder or are on blood thinners, the procedure might carry higher risks, and your eligibility will need to be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
Real-Life Success Stories
Hearing about the experiences of others who’ve undergone stem cell therapy can be incredibly reassuring. Let’s call him mack for short.
When Mack’s motorcycle collided with the pavement, his life changed in an instant. The accident left him with severe injuries—he severed his tricep, broke his glenoid labrum, and broke his hand. The pain was unbearable, and after surgery, it only seemed to intensify. Even more troubling was the uncertainty surrounding his recovery. His doctors were worried he might never regain full mobility, especially given the extent of his injuries.
Before:
Mack was no stranger to challenges, but this was different. The constant, gnawing pain made even the simplest tasks feel insurmountable. Reaching for a glass of water, trying to type on his computer, or even just lying down to rest—it all hurt. He knew that without some kind of breakthrough, his future could be a shadow of the active life he once loved. The prospect of living with this pain indefinitely was daunting, and the thought of not fully recovering weighed heavily on his mind.
After:
Desperate for relief, Mack decided to take a leap of faith. He’d heard about stem cell therapy and its potential to aid in recovery where other treatments might fall short. Just days after his surgery, Mack underwent stem cell injections targeting his injured tricep, labrum, and hand. The change was almost immediate. Within two weeks, Mack noticed a significant reduction in the relentless pain that had plagued him. He could move with greater ease, sleep without discomfort, and—perhaps most importantly—hope began to replace the fear of permanent disability.
Mack’s story is a testament to the power of regenerative medicine. It’s not just about alleviating pain; it’s about reclaiming the life that was nearly lost. Today, Mack is not only back on his feet but steadily regaining the strength and mobility he feared were gone forever. His journey from despair to recovery underscores the incredible potential of stem cell therapy to change lives—especially for those facing the toughest battles.
Conclusion: The Future of Shoulder Pain Treatment
Shoulder pain has long been a challenge for patients and healthcare providers alike. Traditional treatments often come with limitations—whether it’s the slow recovery from surgery or the temporary relief provided by medications. But with the advent of stem cell therapy, we’re witnessing the dawn of a new era in how we approach shoulder pain and injury recovery.
Summary of Benefits
Stem cell therapy isn’t just another treatment option; it’s a groundbreaking approach that offers several distinct advantages over conventional methods:
Non-Invasive: Unlike surgery, stem cell therapy involves no incisions, no lengthy hospital stays, and minimal downtime. This means you can get back to your daily life faster and with fewer complications.
Natural Healing: Stem cells harness the body’s own regenerative capabilities, promoting true healing from within. By addressing the root cause of pain—damaged or degenerated tissue—stem cell therapy offers a more lasting solution rather than just masking symptoms.
Reduced Recovery Time: Traditional surgeries can sideline you for months, but stem cell therapy allows for a quicker recovery, often with noticeable improvements in weeks rather than months.
Lasting Results: Many patients experience not just relief but long-term improvement in mobility and function, reducing the likelihood of recurring issues.
The future of shoulder pain treatment is bright, thanks in large part to the continued development of regenerative medicine. As research progresses, we’re learning more about how stem cells can be utilized not just for shoulder injuries but for a wide array of musculoskeletal issues. The potential is vast: from enhancing recovery times to reducing the need for invasive surgeries, the implications for patient care are profound.
Imagine a world where debilitating shoulder pain no longer hinders your ability to work, play, or simply live comfortably. With each passing year, we move closer to making that vision a reality. As stem cell therapy becomes more refined and accessible, it’s poised to become the standard of care, offering hope to millions who suffer in silence.
Take Your Next Step Towards Healing
If shoulder pain has been a persistent and unwelcome companion in your life, now is the time to explore a treatment that could offer real, lasting relief. Stem cell therapy might be the breakthrough you’ve been waiting for—a way to not just manage your pain but to heal from it.
At Stem Cells LA, we’re committed to helping you reclaim your life from the limitations of pain. Our team is here to provide you with all the information and support you need to make an informed decision about your health. Don’t let another day go by under the shadow of shoulder pain. Reach out to us today to schedule a consultation and discover if stem cell therapy is right for you.
Your journey to recovery starts here—take the first step with us.