Back pain is a pervasive issue that affects millions of people worldwide, significantly impacting their quality of life and productivity. Traditional treatments, such as pain medications, physical therapy, and surgery, often provide only temporary relief and come with various side effects and risks. Lower back pain is amongst the top 3 most burdensome conditions in the United States and is currently the leading cause of work-related disability.
Lower back pain can also be extremely difficult to treat. There are many conditions that cause lower back pain and no individual test that can tell you which one you have. Your doctor can narrow it down, and even give you an idea of your spinal condition, but a lot of back pain conditions are fairly vaguely defined.
This has led to an increasing interest in alternative treatments, particularly in the field of regenerative medicine, which aims to stimulate the body’s natural healing process.
Introduction
Stem cell research has emerged as a promising frontier in medical science, offering new hope for treating chronic back pain. Stem cell treatment, in particular, has shown potential in addressing the root causes of back pain by aiming to rebuild damaged tissue, promote disc regeneration, alleviate pain, and restore function. This article explores the role of stem cell therapy in treating back pain, its procedures, benefits, and future prospects.
Understanding Back Pain

Common Causes of Back Pain
Muscle Strain or Sprain: Overuse, heavy lifting, or awkward movements can strain or sprain muscles and ligaments in the back, causing acute or chronic pain.
Herniated or Bulging Discs: Discs act as cushions between the vertebrae of the spine. When a disc becomes damaged and presses on nerves, it can cause significant pain, commonly known as a herniated or bulging disc.
Degenerative Disc Disease: Over time, the intervertebral discs can wear down, lose their cushioning ability, and lead to pain and stiffness. This is a common cause of chronic back pain in older adults.
Spinal Stenosis: This condition occurs when the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness.
Sciatica: When the sciatic nerve is compressed, often by a herniated disc or bone spur, it can cause sharp, shooting pain that radiates from the lower back down through the leg.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can also cause back pain.
Scoliosis: This abnormal curvature of the spine can cause back pain and affect posture and mobility.
Osteoporosis: This condition weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures, including in the vertebrae, which can cause significant back pain.
Poor Posture: Chronic poor posture, especially when sitting for long periods, can strain the back muscles and spine, leading to pain and discomfort.
Injuries: Trauma from accidents, falls, or sports injuries can cause immediate and sometimes long-lasting back pain.
Medical Conditions: Conditions such as kidney stones, infections, or tumors can also cause back pain, though these are less common.
Impact of Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease primarily affects the intervertebral discs, leading to several notable impacts on the spine and overall well-being:
Disc Structure and Function: Intervertebral discs consist of a tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and a gel-like inner core (nucleus pulposus). Over time, these discs can lose water content and structural integrity, causing them to flatten or bulge. This structural compromise diminishes their ability to absorb shock and support spinal movement effectively.
Pain and Inflammation: Degeneration of discs can result in chronic pain localized to the affected area or radiating to adjacent regions. Inflammation may develop as a response to structural changes and disc degeneration. The inflammatory process can irritate nearby nerves and tissues, exacerbating pain signals and causing discomfort that may radiate through the back and into the limbs.
Reduced Mobility and Functionality: As discs degenerate, the spine’s flexibility and range of motion may decrease. This can limit daily activities, such as bending, twisting, or lifting, and impact overall physical functionality. Reduced mobility contributes to muscle stiffness, weakness, and challenges in maintaining posture.
Neurological Implications: In severe cases, degenerative changes in discs, such as herniation or compression, can exert pressure on adjacent spinal nerves. This compression may lead to neurological symptoms like numbness, tingling, or weakness in the extremities. Additionally, disc herniation can cause pinched nerves or spinal cord compression, necessitating medical intervention to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Impact on Facet Joints: Degenerative changes in discs can alter spinal alignment and place additional stress on facet joints, which facilitate spinal stability and movement. Over time, facet joint degeneration may contribute to localized pain, stiffness, and joint dysfunction, further complicating the management of degenerative disc disease.
Challenges of Traditional Treatments
Traditional treatments for back pain, such as pain medications, physical therapy, and surgery, often provide limited relief and come with significant risks and side effects. These treatments typically focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the underlying causes of pain.
Traditional treatments have been known to “work,” but there’s almost always a catch with it, like “you’ll be able to stand up straight again, but your going to have “blank” in your back to support it…so you won’t be able to bend fully like you used to.” To the patients suffering, it may seem like good news, but is it really?
Stem Cell Therapy Overview
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are unique cells found throughout our bodies with the ability to support and even develop into different types of cells. Bone marrow stem cells, harvested from the patient’s bone marrow, are used in intradiscal injections to repair, restore, and regenerate damaged tissues in the lower back, offering potential benefits for back pain treatment. Mesenchymal stem cells, in particular, have shown a lot of promise in regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into bone, cartilage, and even muscle cells, making them ideal for repairing damaged tissues.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are remarkable for their ability to contribute to tissue repair and regeneration in the body. Here’s how they work:
Migration to Injury Sites: MSCs have the capability to migrate towards sites of tissue injury or inflammation. Once they reach these areas, they play a crucial role in initiating the healing process.
Differentiation into Specialized Cells: MSCs possess the unique ability to differentiate into various types of cells depending on the surrounding microenvironment. For instance, they can transform into bone cells (osteoblasts), cartilage cells (chondrocytes), or fat cells (adipocytes) as needed for tissue repair.
Release of Growth Factors: MSCs secrete a variety of bioactive molecules, including growth factors and cytokines, that have several beneficial effects:
Promotion of Tissue Regeneration: Growth factors released by MSCs stimulate nearby cells to proliferate and differentiate, aiding in the regeneration of damaged tissues.
Reduction of Inflammation: MSCs have anti-inflammatory properties. They can modulate immune responses by suppressing excessive inflammation, thereby reducing tissue damage and promoting a conducive environment for healing.
Support for Neighboring Cells: MSCs provide support to neighboring cells by promoting their survival and enhancing their functional capabilities.
4. Modulation of Immune Responses: MSCs can interact with immune cells in the body, influencing their activity. They can inhibit the proliferation of certain immune cells and promote the generation of regulatory immune cells that help maintain immune balance and tolerance.
5. Paracrine Effects: In addition to their direct involvement in tissue repair through differentiation, MSCs exert paracrine effects. This means they influence the behavior of neighboring cells through the secretion of signaling molecules, even if they do not directly differentiate into those cell types.
6. Promotion of Angiogenesis: MSCs can stimulate the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) in damaged tissues. Improved blood supply enhances nutrient and oxygen delivery to the site of injury, supporting tissue repair and regeneration.
Overall, they are great for regenerative medicine and therapeutic applications in treating various conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders, inflammatory diseases, and injuries. Their ability to migrate, differentiate, and secrete bioactive factors underscores their role.
Stem Cell Research and Back Pain
Recent research has demonstrated the potential of stem cells in treating back pain. Studies have shown that stem cell therapy can help regenerate damaged intervertebral discs, reduce inflammation, and provide long-lasting pain relief.
Stem Cell Procedures for Back Pain
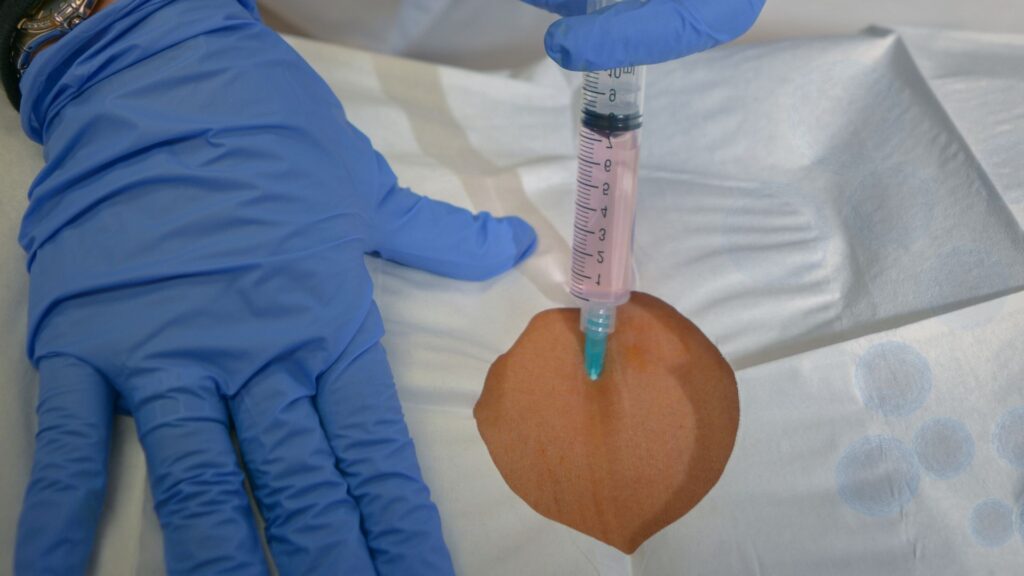
Overview of Stem Cell Injections
Stem cell injections involve either harvesting stem cells from the patient’s own body, typically from bone marrow or adipose tissue, or utilizing donor stem cells, and injecting them into the affected area. Bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC) involves extracting stem cells from the patient’s bone marrow and injecting them to promote natural healing and pain relief. This minimally invasive procedure aims to promote healing and regeneration of damaged tissues.
Intradiscal Stem Cell Injections
An intradiscal injection involves administering medication directly into the spinal disc. When it comes to intradiscal stem cell injections, doctors harvest stem cells from the patient’s bone marrow, which is rich in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and inject them into the damaged spinal disc. These injections also utilize growth factor-rich platelets, which play a crucial role in stimulating the body’s natural healing process and aiding in the rebuilding of damaged tissue. Intradiscal stem cell injections can be considered when conventional treatments have not effectively reduced symptoms or cured the condition. First-line treatments for back pain typically include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, traction, and physical therapy.
Minimally Invasive Treatment
One of the significant advantages of stem cell therapy is its ability to reduce pain due to its minimally invasive nature. Unlike traditional surgeries, stem cell injections do not require large incisions, reducing the risk of complications and shortening recovery time.
Rebuilding Damaged Tissue
Stem cells have the unique ability to rebuild damaged tissue, including intervertebral discs. This regenerative capability is crucial for treating chronic back pain, as it addresses the root cause rather than merely managing symptoms.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy

Stem cell therapies have shown promising results in studies regarding pain relief and improved function for back and spinal pain. These therapies are becoming increasingly popular due to their potential to regenerate damaged tissues and provide long-term relief. The viability and effectiveness of stem cell therapy can vary depending on the patient’s condition, but many have reported significant improvements.
Pain Relief and Improved Mobility
Patients undergoing stem cell therapy for back pain often report significant pain relief and improved mobility. By promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation, stem cells provide a more comprehensive solution to back pain.
Reduced Recovery Time
Compared to traditional surgical treatments, stem cell therapy offers a shorter recovery time. Patients can often return to their daily activities much sooner, with less postoperative pain and discomfort.
Long-Term Benefits
Stem cell therapy not only provides immediate pain relief but also offers long-term benefits. By regenerating damaged tissues, it addresses the underlying issues, potentially preventing the recurrence of back pain.
Success Stories and Patient Outcomes

Case Studies and Testimonials
Many patients have experienced positive outcomes with stem cell therapy for back pain. Case studies and testimonials highlight significant improvements in pain levels, mobility, and overall quality of life. These success stories underscore the potential of stem cell therapy as a viable treatment option. At Stem Cells LA, we take care of our patients and make sure that they know what they are getting into before they commit.
Comparative Effectiveness
Studies comparing stem cell therapy with traditional treatments have shown promising results. Stem cell therapy often outperforms conventional methods in terms of pain relief, recovery time, and long-term outcomes, making it an attractive alternative for patients seeking lasting solutions.
The Future of Back Pain Treatment
Advancements in Regenerative Therapy
The field of regenerative therapy is continually evolving, with ongoing research and advancements promising even more effective treatments for back pain. Innovations in stem cell therapy, such as enhanced cell delivery methods and improved understanding of stem cell biology, are expected to further improve patient outcomes.
Ongoing Research and Potential Breakthroughs
Researchers are exploring new ways to enhance the efficacy of stem cell therapy for back pain. Potential breakthroughs include the use of genetically modified stem cells, combination therapies, and advanced imaging techniques to ensure precise cell delivery.
Broader Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
While this article focuses on back pain, stem cell therapy has broader applications in treating various chronic pain conditions and injuries. As research progresses, stem cell therapy may become a standard treatment for a wide range of musculoskeletal issues.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy offers a promising alternative for treating chronic back pain. By addressing the root causes of pain and promoting tissue regeneration, it provides significant pain relief, improved mobility, and long-term benefits. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure further enhances its appeal.
If you are suffering from chronic back pain, consider consulting with a medical professional about the potential benefits of stem cell therapy. Stay informed about the latest developments in stem cell research and explore this innovative treatment option for a better quality of life.
References and Further Reading
If you don’t believe us, check out what the Mayo Clinic has to say about the safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC’s) for lower back pain, here.